This article explains how to diagnose issues with unsigned drivers in 64-bit versions of Windows, which can prevent the system from booting and cause a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD). The issue can be temporarily bypassed by disabling driver signature enforcement during boot (F8 > Disable Driver Signature Enforcement). The example is based on Windows Server 2008 R2, but the methodology applies to other 64-bit versions, such as Windows 7 x64 and Vista x64.
Background of the Issue
Microsoft introduced mandatory driver signature verification starting with Windows Vista for 64-bit versions. If a driver lacks a digital signature, the system cannot load it, resulting in a critical error and a BSOD. The specific error code depends on the blocked driver.
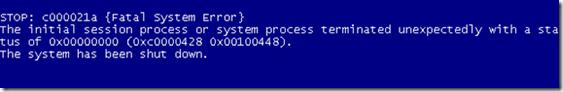
Example of an error you may encounter:
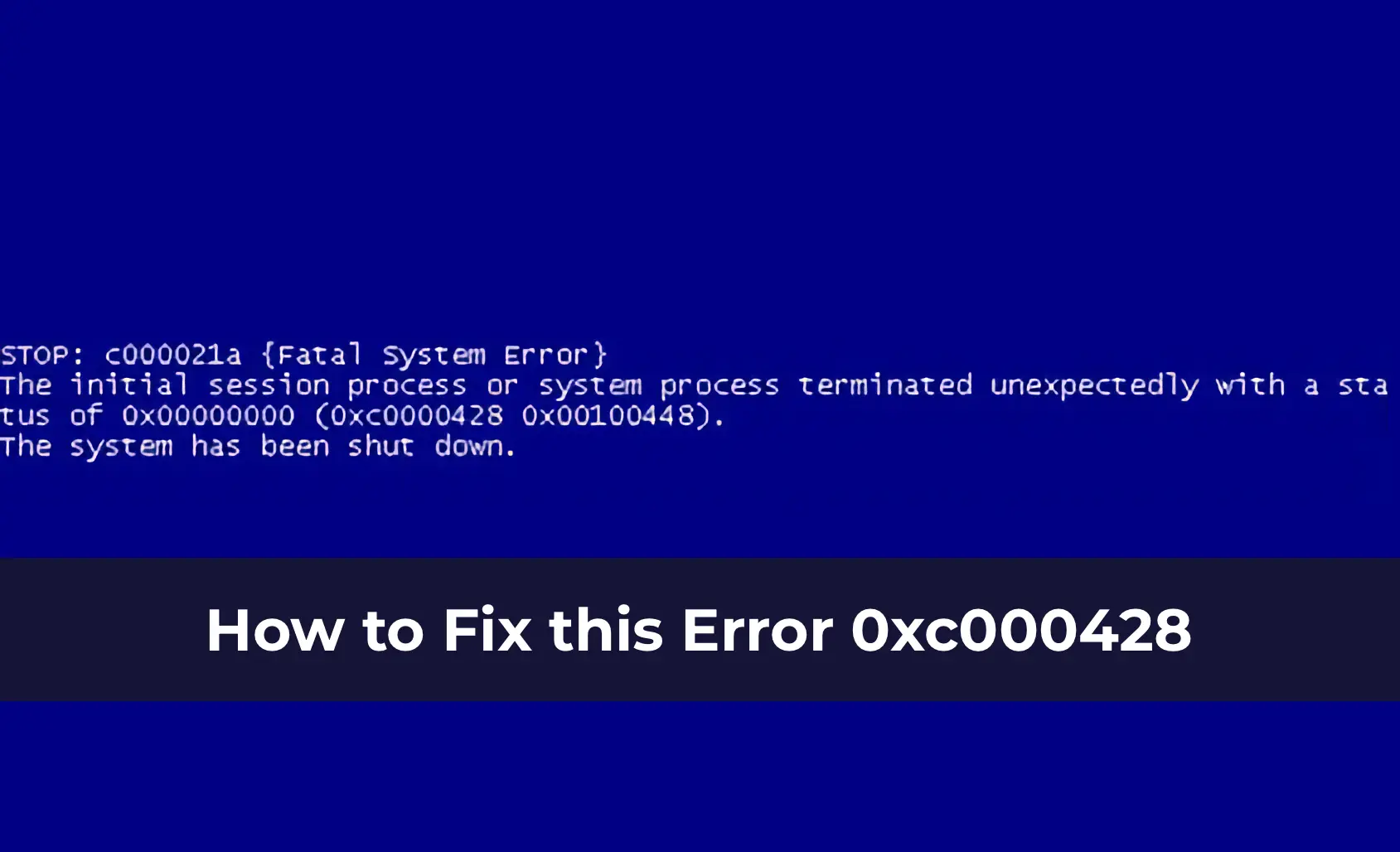
STOP: c000021a (Fatal System Error)
The initial session process or system process terminated unexpectedly with a status of 0x00000000 (0xc000428 0x00100448).
The error 0xc000428 indicates that Windows cannot verify the digital signature of a driver.
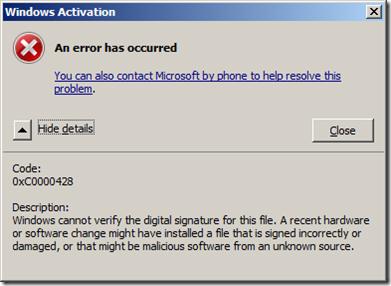
To convert the hexadecimal error code into a more readable form, you can use the built-in Windows utility SLUI.EXE or cross-reference the error code in the ntstatus.h file, which is available in the Windows SDK. We’ll use the first method by running the following in the Command Prompt:
As shown in the screenshot, we confirmed that the BSOD is caused by the inability to verify the digital signature of a driver (“Windows cannot verify digital signature for this file”).
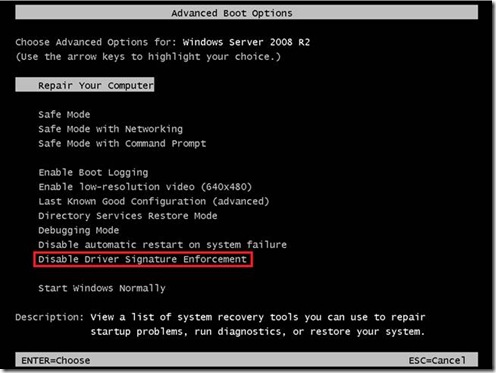
Step 1: Disabling Driver Signature Enforcement
To diagnose the issue, boot the system with driver signature enforcement disabled:
1. Reboot the computer.
2. Press F8 during boot and select Disable Driver Signature Enforcement from the Advanced Boot Options menu.
If the system boots without errors, this confirms the presence of an unsigned driver causing the boot failure.
Step 2: Identifying the Problematic Driver
To pinpoint the driver causing the crash, check the Event Log:
1. Open Event Viewer and navigate to Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > CodeIntegrity > Operational.
2. Look for an event with EventID 3001, which will specify the driver that failed the digital signature check.
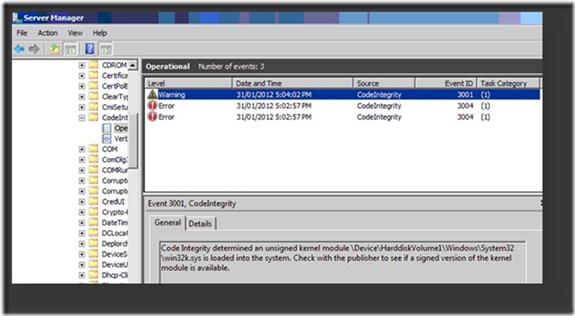
Example message:
Code Integrity determined that an unsigned kernel module \Device\HarddiskVolume1\Windows\System32\win32k.sys is loaded into the system.
Step 3: Verifying the Driver’s Signature with Sigcheck
To confirm that the specified driver is unsigned, use the sigcheck.exe utility from Sysinternals:
1. Download sigcheck.exe from Microsoft’s website.
2. Run the command:
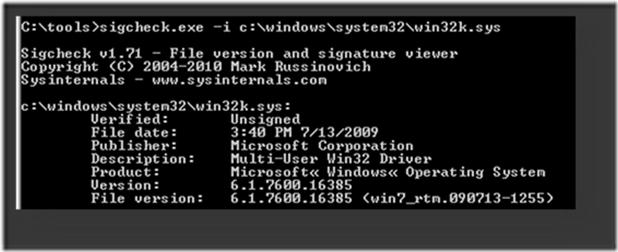
sigcheck.exe -i c:\Windows\System32\win32k.sys
If the driver is unsigned, the Verified field will display Unsigned.
Step 4: Resolving the Issue
Once the problematic driver is identified, you have several options to resolve the issue:
1. Find a signed version of the driver.
– Visit the hardware manufacturer’s website to download the latest digitally signed driver version.
2. Stop using the driver.
– If the device is not critical to system operation, you can disable or uninstall the driver.
Step 5: Identifying the Device Associated with the Driver
To precisely identify the device linked to the problematic driver, use the Registry Editor:
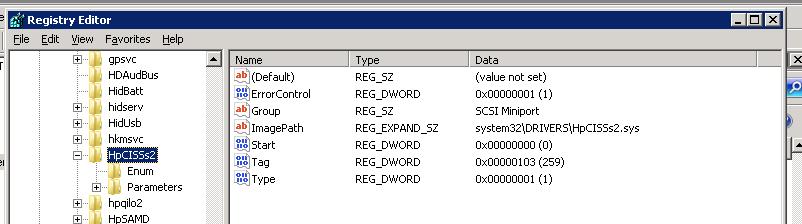
1. Open regedit and locate the driver’s value under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\services.
2. In the ENUM section, the device code will be listed (e.g., PCI\VEN_103C&DEV_3230).
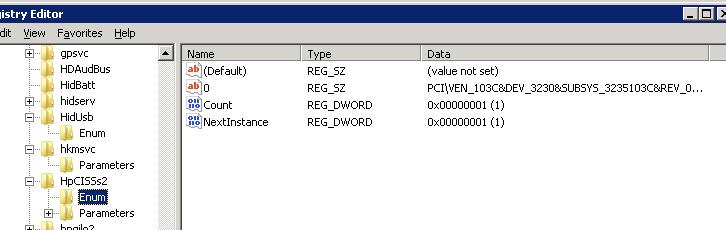
3. Using the VEN (vendor) and DEV (device) codes, identify the specific hardware.
4. Determine that the device vendor has ID 103C and the device code is 3230.
5. Visit devicehunt.com (or a similar device ID lookup site) and enter the found Vendor and Device codes in the respective fields.
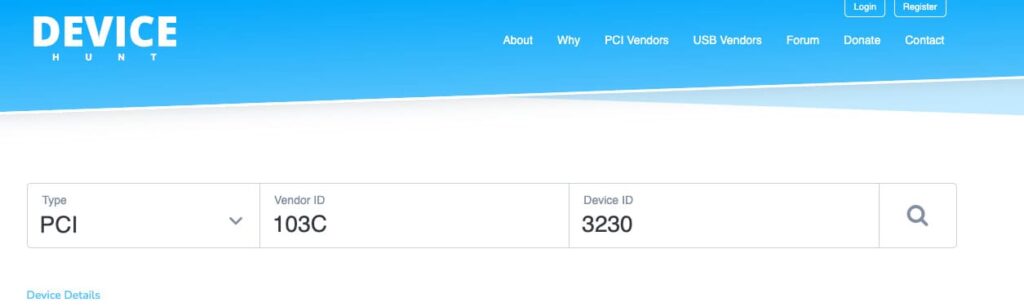
6. Scroll down and locate the PCI device with vendor ID 103C and device code 3230, which corresponds to an HP Smart Array Controller.

Finally, locate the latest driver version on the hardware manufacturer’s website (ensure the driver is compatible with your OS version) and update the driver on your computer.
Issues with unsigned drivers can prevent the system from booting. By using tools to verify digital signatures and Windows diagnostic utilities, you can identify the problematic driver and resolve the error by either updating to a signed driver version or disabling the driver.