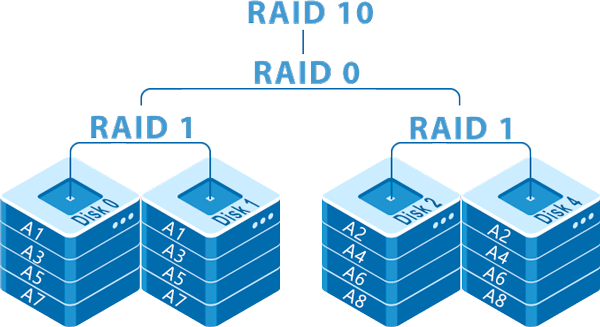
RAID 10 (Redundant Array of Independent Disks, Level 10) — a combination of two RAID technologies: RAID 1 (mirroring) and RAID 0 (striping). This solution provides both high performance and fault tolerance. RAID 10 is sometimes referred to as RAID 1+0, as the array is built from multiple mirrored pairs combined into a striped array.

Mirroring (RAID 1):
Data is simultaneously copied to two disks (a mirrored pair).
For example, in a 4-disk array, disks 1 and 2 form the first mirrored pair, and disks 3 and 4 form the second.
Striping (RAID 0):
Data is then distributed (striped) across the mirrored pairs.
This means data blocks are written across both mirrored pairs, enhancing read and write performance.
Minimum Number of Disks:
RAID 10 requires a minimum of 4 disks (2 mirrored pairs).
Fault Tolerance:
The array can withstand the failure of one disk in each mirrored pair.
If two disks in the same pair fail, data will be lost.
Performance:
Read: High speed, as data can be read simultaneously from multiple disks.
Write: Write speed is higher than RAID 1 due to striping.
Fault Tolerance:
– Data is securely protected, as each write is duplicated.
High Performance:
– RAID 10 combines the fast read and write benefits of RAID 0 with the reliability of RAID 1.
Ease of Recovery:
– Data recovery after a single disk failure is fast, as data only needs to be copied from the mirrored disk.
Flexibility:
– RAID 10 is suitable for database servers, applications with intensive read/write operations (e.g., virtualization, transaction processing).
High Storage Costs:
– Half of the array’s capacity is used for mirroring, reducing overall storage.
Minimum Number of Disks:
– RAID 10 cannot be created with fewer than 4 disks.
Complex Configuration:
– Setting up RAID 10 is more complex than RAID 1 or RAID 0.

RAID 10 can be created on Windows using built-in tools, third-party software, or a hardware RAID controller.
1. Using Storage Spaces
Storage Spaces — a disk management tool in Windows that enables the creation of fault-tolerant arrays.
2. Using a Hardware RAID Controller
Suitable RAID Controllers:
– Adaptec (7805, 8805 series),
– LSI MegaRAID,
– Dell PERC,
– HP Smart Array Controllers.

3. Using Third-Party Software
If a hardware RAID controller is unavailable, software solutions can be used:
– SoftRAID for Windows: Supports RAID 10 creation through a user-friendly interface.
– StableBit DrivePool: Software for managing and creating RAID arrays with mirroring and striping.
– DiskInternals RAID Recovery: Primarily for recovery but can be used to create software arrays.
4. Using Windows Built-in Disk Management
Windows 10 and Windows Server support mirroring (RAID 1) but do not natively support RAID 10. To implement:
– Create two mirrored pairs (RAID 1).
– Configure them as a single RAID 0 array using Storage Spaces.