We’ll also cover how to configure shared folders for seamless file exchange between devices.
Looking to purchase genuine Windows Server RDS product keys? Check out our catalog from 14.80 €
Step 1: Installing Windows App
Make sure you’re logged into your Mac account to download apps from the App Store.
1. Open the App Store on your MacBook.
2. Search for Windows App (formerly Microsoft Remote Desktop).
3. Install the app. It’s free and works perfectly for remote management of Windows computers.
4. After installation, click Open to launch the app.
Step 2: Setting Up the Connection
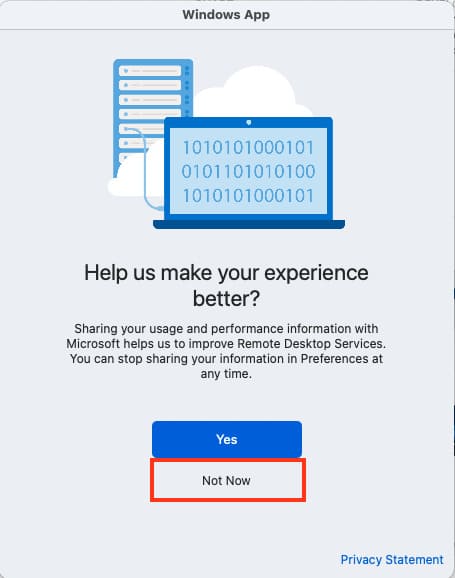
Once the app opens, click Not Now to skip the tutorial window.
You’ll see an empty app window.

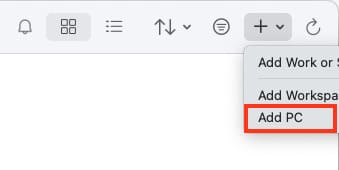
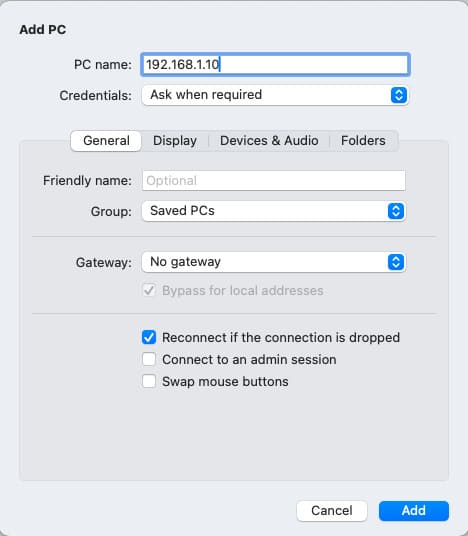
1. Click the + in the top-right corner, then select Add PC in the main app window.
2. In the PC Name field, enter the IP address of the remote Windows computer.
3. Click Add.
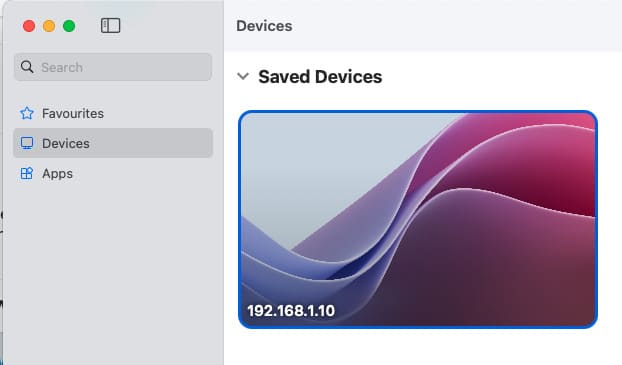
4. Double-click the added computer to connect.
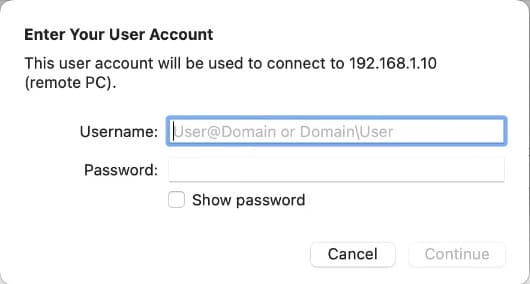
When connecting, enter the Windows user’s login and password. If a certificate warning appears, simply confirm the connection.
5. After this, you’ll be connected to your PC’s desktop via RDP.
Step 3: Configuring Shared Folders
To enable file sharing between your MacBook and the remote computer, follow these steps:
1. Close the current connection session.
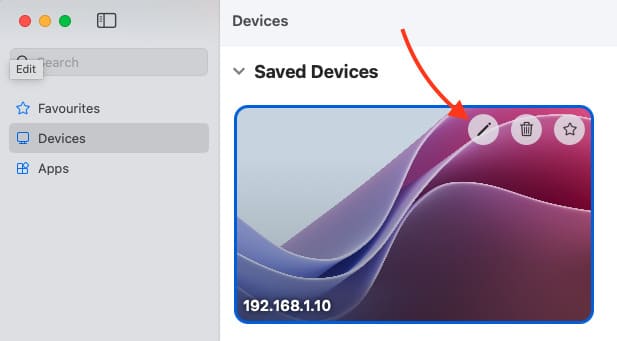
2. In the Windows App, select the previously added computer and click Edit.
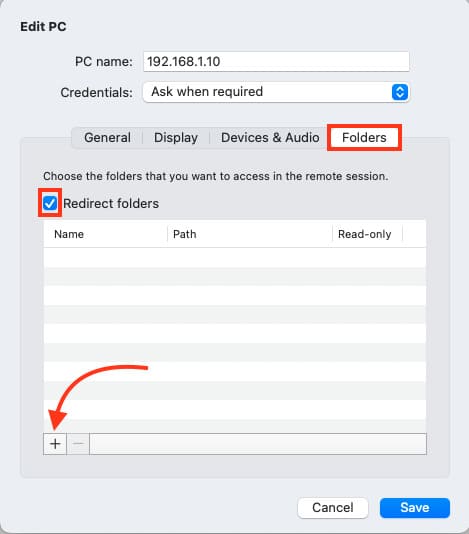
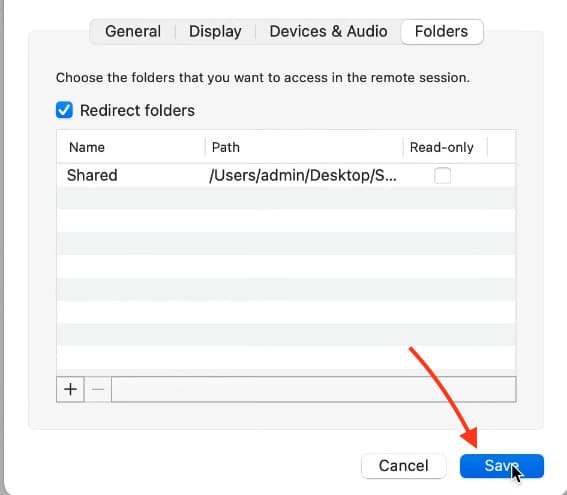
3. Go to the Folders section.
4. Click + to add a shared folder. For example, create a folder on your desktop named Shared.
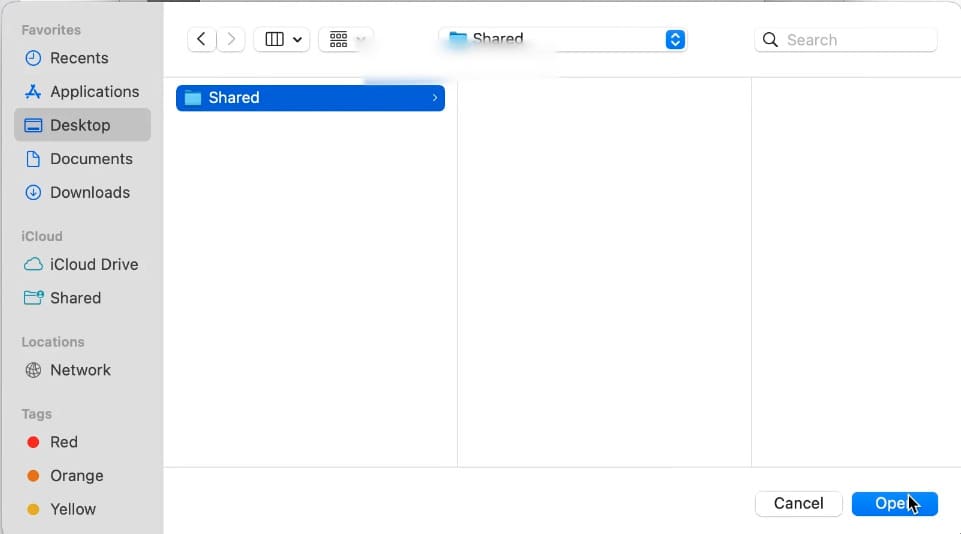
5. Select the created folder and click Open.
6. Save the changes by clicking Save.
Step 4: Exchanging Files
1. Reconnect to the remote computer.
2. Open Windows Explorer and navigate to This PC.
3. You’ll see the Shared folder linked to your MacBook.
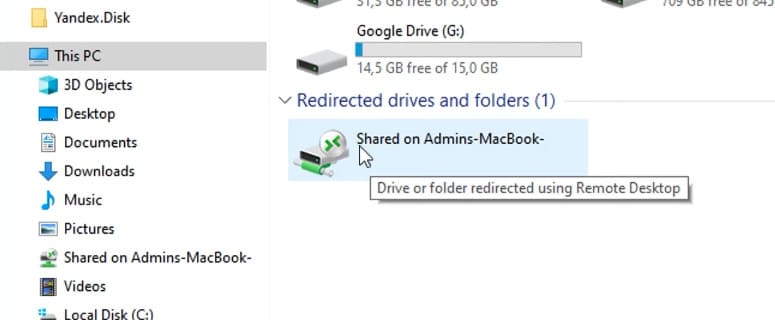
4. Drag and drop the desired file into this folder to transfer it to your MacBook or vice versa.
Files will transfer quickly if the devices are on the same network.
With the Windows App, you can easily manage a remote Windows computer and set up file sharing between devices. This method is simple to configure and saves time when working across different operating systems.