This article explains how to remotely power on computers in a local network using Wake-on-LAN (WOL) technology. This is a convenient solution for system administrators who need to perform backups, install updates, and other operations at night without leaving computers powered on continuously.
What is Wake-on-LAN?
Wake-on-LAN (WOL) technology allows you to remotely power on a computer over a network, even if it is turned off or in sleep mode. To do this, send a special network packet called a “Magic Packet,” containing the unique MAC address of the network card, to activate only the desired computer.
A computer supporting Wake-on-LAN supplies power to the network card even when off. The network card analyzes all network traffic and, upon receiving the Magic Packet, powers on the computer. This technology is supported by most modern network cards and motherboards.
Requirements for Wake-on-LAN
1. Access to the local network where the target computer is located. If the PC is outside the local network, port forwarding on the router is required.
2. A motherboard and network card supporting Wake-on-LAN. In some cases, connect the special “WOL” cable from the network card to the motherboard.
3. Enable WOL support in the BIOS. Options may include:
– MAC Resume From S3/S4
– PME Events Wake Up
– Power On By Onboard LAN
– Resume by LAN
– Wake On LAN from S5
Check the network card properties in Device Manager under the Power Management tab to ensure power-on options are enabled.

Some network cards support additional wake-up settings.

Remote PC Wake-Up Over the Internet
To wake up a computer remotely over the internet, use online services to send the Magic Packet. Here are two popular services:
1. Depicus Service
– Visit the official Depicus website.
– Enter the computer’s MAC address and IP address (typically the router’s public IP).
– Click “WAKE UP”.

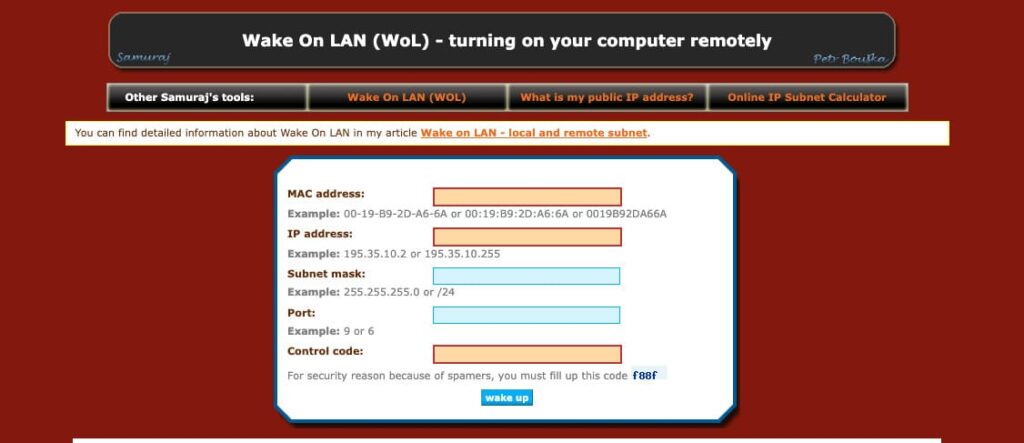
2. Samuraj-cz.com Service
– Visit the official Samuraj-cz.com website.
– Enter the public IP address, computer’s MAC address, and port, then click “Send”.
Applications for Remote PC Wake-Up
For Windows
To wake up a PC over a local network, use the WakeMeOnLan application for Windows. It supports managing multiple devices and works via the command line.

Command-line examples:
– Wake up by IP address:
WakeMeOnLan.exe /wakeup 192.168.2.1
– Wake up by name:
WakeMeOnLan.exe /wakeup PC01
– Wake up by MAC address:
WakeMeOnLan.exe /wakeup 12-34-45-78-90-AB
For Linux
On Linux, use the etherwake utility to send the Magic Packet. Install it with:
– For CentOS/RedHat:
yum -y install etherwake
– For Debian/Ubuntu:
aptitude install etherwake
Example usage:
etherwake 12-34-45-78-90-AB
For Android
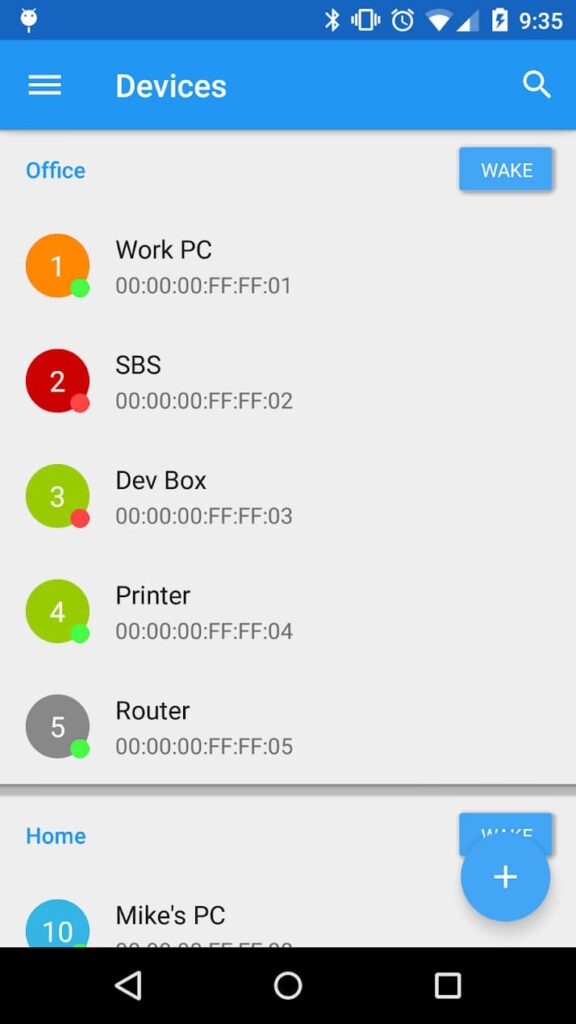
To wake up a computer from an Android phone, use the Wake On Lan app:
– Download it from Google Play.
– Enter the IP and MAC address of the target computer and click the wake-up button.
Verifying Wake-on-LAN Functionality
To ensure the setup works, use the Wake On Lan Monitor utility for Windows. It checks if the network card receives the Magic Packet.
– Download the utility directly from the official Depicus website.
– Launch the utility, select the UDP port, and click “Start”.

– After clicking “Start”, the label “Disconnected” will change to “Connected”. This means the application is listening on the specified port for the Magic Packet.

– After sending the Magic Packet, the application will display information about its receipt.
If the Magic Packet is received (the log line should contain the target computer’s MAC address following “FF FF FF FF FF FF”), the computer should power on.