In this article, we will explain how to use the msconfig utility for configuring and diagnosing Windows. We will cover the main functions of msconfig, ways to launch it, and usage scenarios to improve your system’s performance.
msconfig – Instruction and Setup
Msconfig is a built-in utility designed to identify the causes of system and application malfunctions, choose Windows boot options, and diagnose the system. Many beginner PC users mistakenly look for where to download msconfig, not knowing that it is already installed by default in Windows. Below are several ways to launch it on different versions of Windows.
Ways to Launch msconfig
First Method (Suitable for Windows Vista, 7, 8, 10) – The Fastest
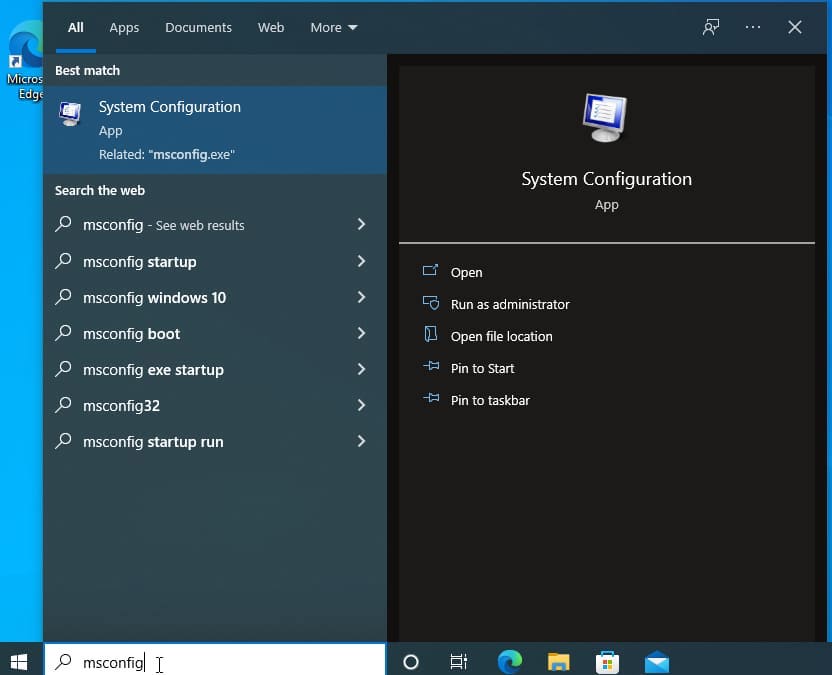
If you have Windows Vista, 7, 8, 8.1, or 10, simply click on the “Start” menu and type msconfig. Press Enter.
Second Method (Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10)
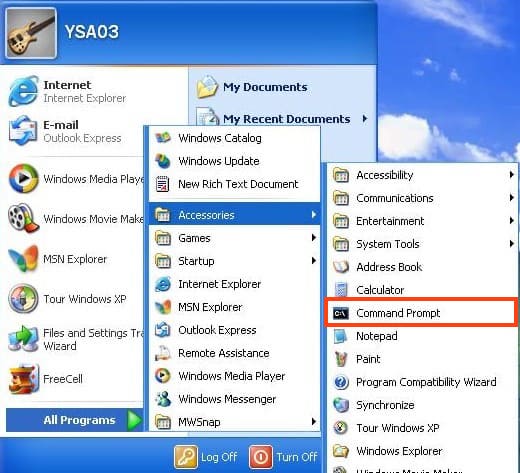
Go to the Start – All Programs – Accessories menu. Select “Command Prompt”.
A black command prompt window will appear, where you type msconfig and press Enter.
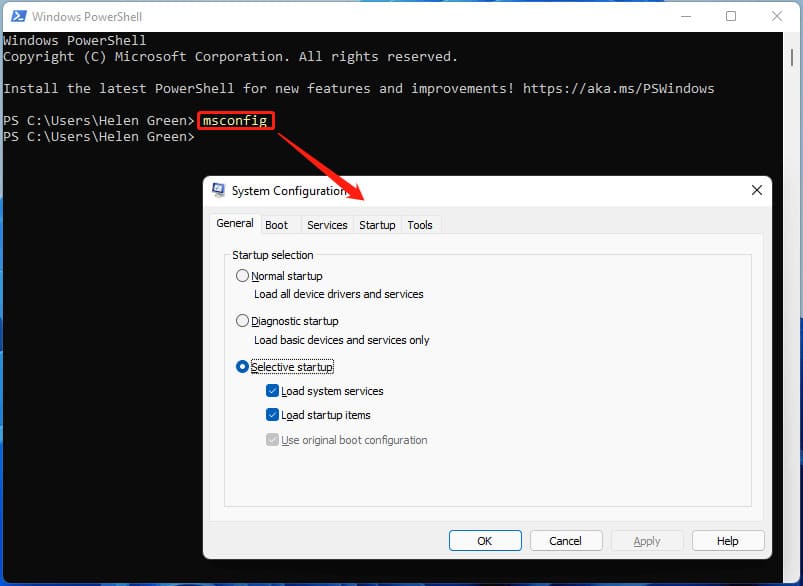
Third Method (Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10)
Click “Start”, then “Run” and type msconfig. Press Enter.
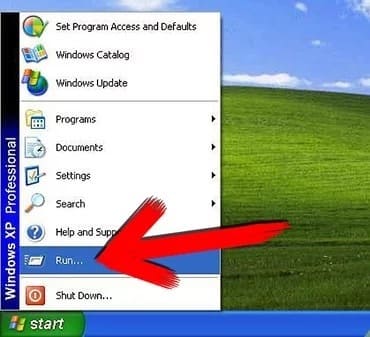
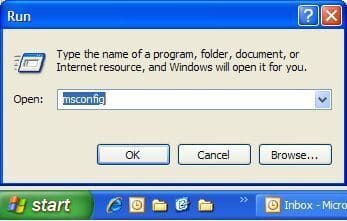
Fourth Method (Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10)
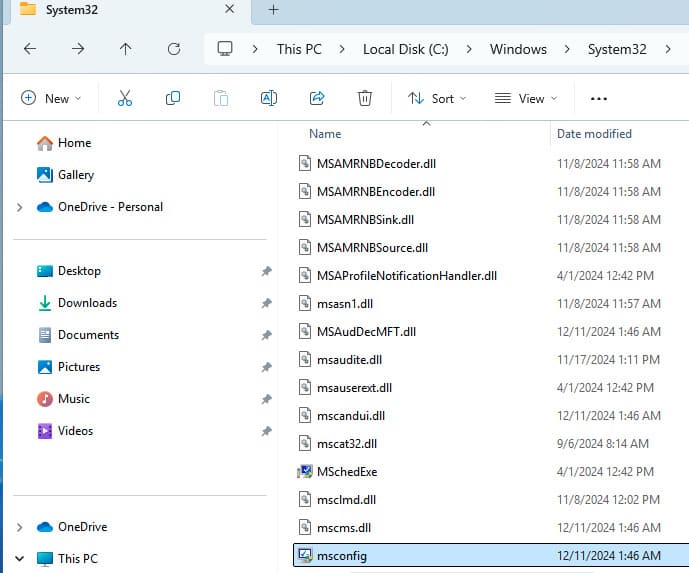
Navigate to C:\Windows\System32 in File Explorer and find the msconfig.exe file.
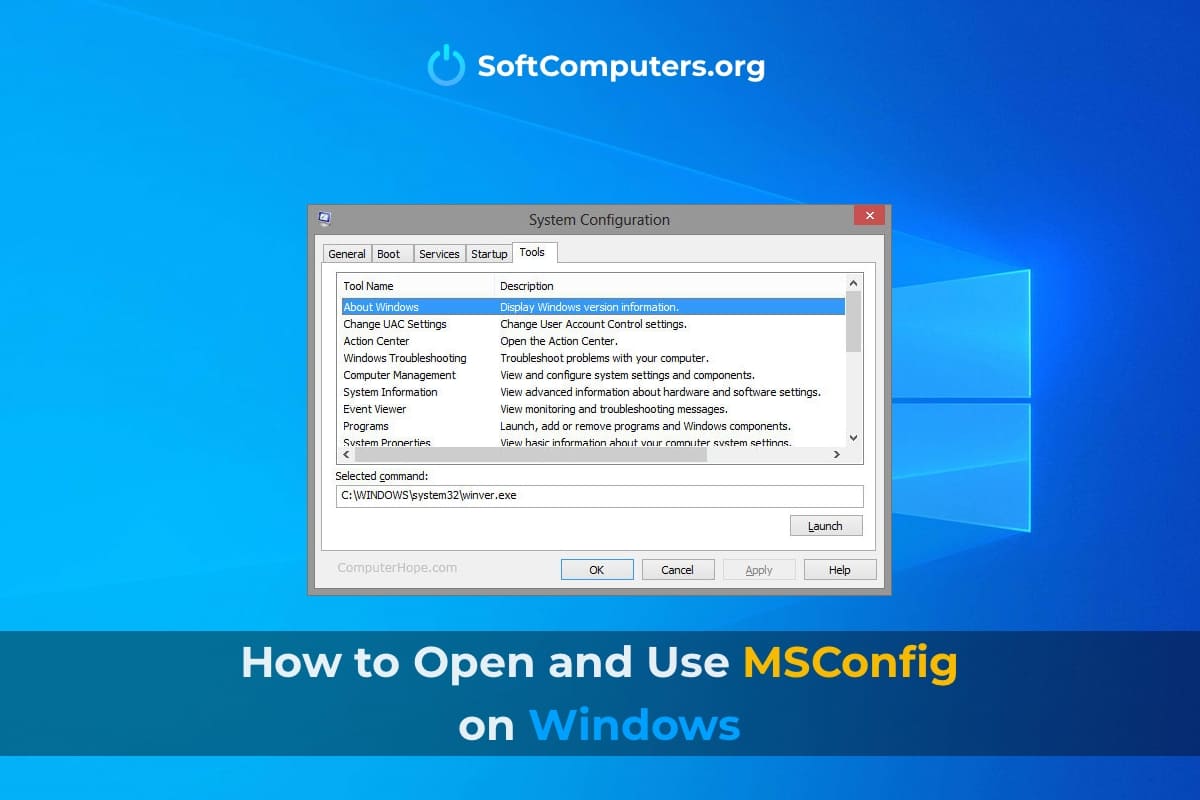
msconfig Utility
The msconfig interface consists of five tabs: General, Boot, Services, Startup, Tools. Let’s examine each of them in detail.
General
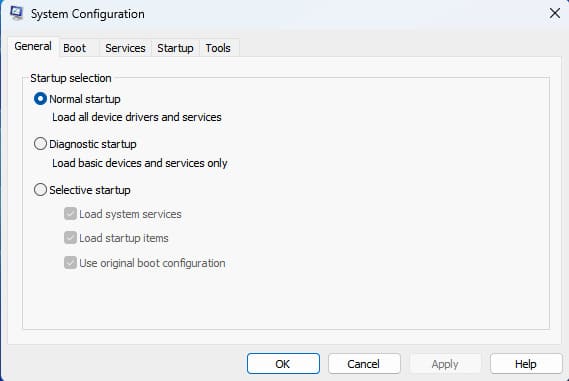
– Normal Startup: loads all drivers, system services, and startup applications.
– Diagnostic Startup: loads only essential drivers and system services.
– Selective Startup: allows flexible system load configuration, including selecting system services and startup applications.
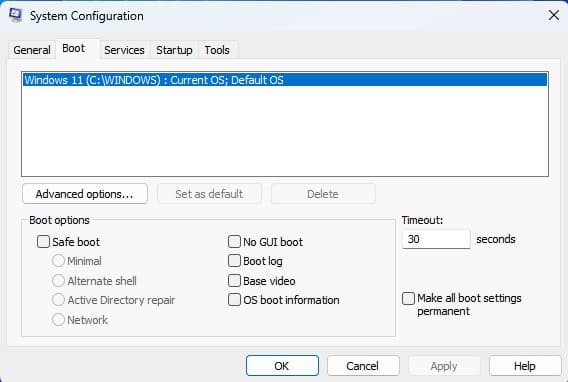
Boot
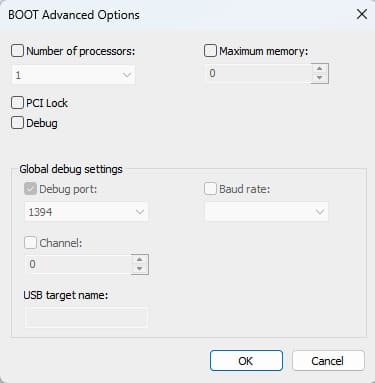
This tab allows you to manage OS boot settings: choose the default system, set the OS selection timeout, and use additional boot parameters (e.g., limit the number of CPU cores or memory).
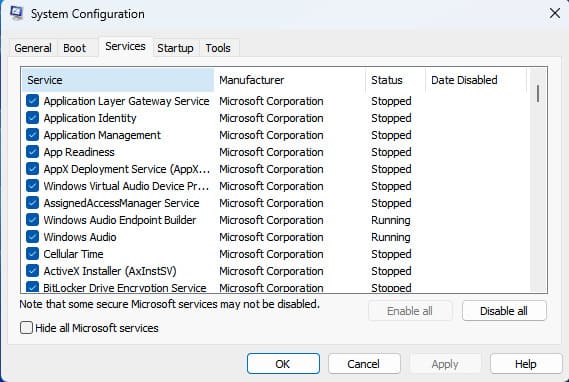
Services
In this tab, you can enable and disable system and third-party services. For convenience, you can hide Microsoft services to view only third-party ones.
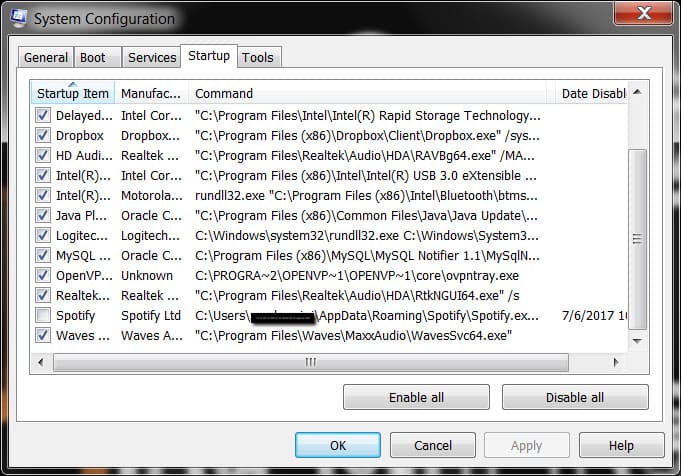
Startup
This tab allows you to manage applications that start with the system. Disabling unnecessary applications helps reduce system boot time.
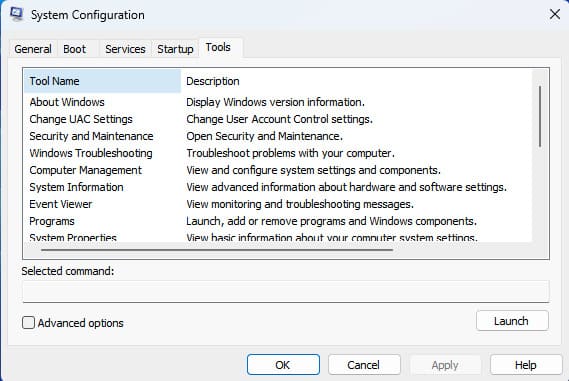
Tools
Here you will find a list of administration and system diagnostics utilities. You can launch them directly from the msconfig window.
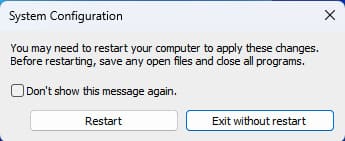
If you make any changes and click the “OK” button, a window like this will appear:
Main Usage Scenarios for msconfig
Debugging and Troubleshooting
Msconfig helps diagnose startup and system operation issues. You can use diagnostic startup and selective startup to gradually enable services and applications to identify the cause of malfunctions.
Testing
With msconfig, you can limit the number of active CPU cores or the amount of RAM to test system or application performance under such conditions. Regularly check the “Services” and “Startup” tabs to disable unnecessary services and applications that slow down system boot.