Active Directory Group Policies (GPO) enable centralized management of computer and user settings in a domain environment, greatly simplifying administration. The Group Policy Management Console (GPMC.msc) is the primary tool for managing group policies in Active Directory.
You can purchase original Windows Server product keys from our store from 10.80 €
Download Windows Server installers from our catalog.
Installing the GPMC Console in Windows
In Windows 10 and 11, the GPMC console is included in the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) and can be installed through the Settings panel.
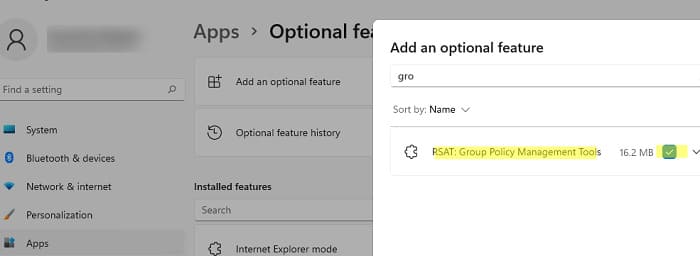
Navigate to Settings => Apps => Optional Features => Add an optional feature, select RSAT: Group Policy Management Tools from the list, and click Install.
You can also install the Group Policy Management Console in Windows 10 and 11 using PowerShell:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.GroupPolicy.Management.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Or using DISM:
DISM.exe /Online /add-capability /CapabilityName:Rsat.GroupPolicy.Management.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
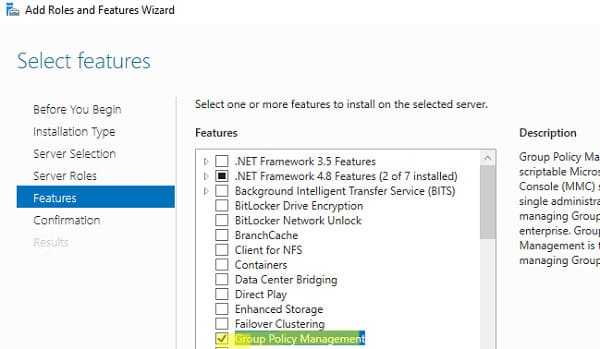
In Windows Server 2022/2019/2016/2012R2, you can install the GPMC console via Server Manager:
Add Roles and Features => Features => Group Policy Management.
Alternatively, install the GPMC console in Windows Server using a PowerShell cmdlet:
Install-WindowsFeature GPMC

After installation, verify that the Group Policy Management shortcut appears in the Administrative Tools section of the Control Panel (Control Panel\System and Security\Administrative Tools). The shortcut points to the MMC snap-in:
%SystemRoot%\system32\gpmc.msc

Managing Active Directory Group Policies with the Group Policy Management Console
The GPMC console allows management of group policies at the level of Active Directory sites, domains, and Organizational Units (OUs).
To launch the console, run:
gpmc.msc
By default, the console connects to the domain controller holding the Primary Domain Controller Emulator (PDC) role. You can connect to any other DC by right-clicking the domain name and selecting Change Domain Controller.
Expand Forest => Domain => Your Domain.

The Group Policy Management console screenshot highlights:
– The domain name to which the console is connected.
– Group policies assigned to various OUs.
– The full list of policies (GPOs) in the current domain, available under Group Policy Objects.
To create a new GPO and link it to an OU, right-click the desired container and select Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here.

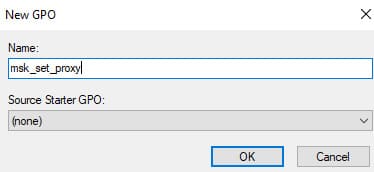
Specify a name for the GPO:
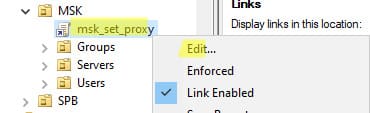
In the GPMC console, you will see the new GPO, which is automatically linked to the selected container. The policy is active (Link Enabled = True), meaning its settings will apply to all objects in the OU.
To modify the GPO settings, select Edit.
This opens the GPO editor console, similar to the local GPO editor. All GPO settings are divided into two sections:
– Computer Configuration — settings for computers.
– User Configuration — settings for Active Directory users.
Each section contains three subsections:
– Software Settings — used for installing and updating software via GPO.
– Windows Settings — includes core Windows security settings: password policies, account lockout policies, audit policies, user rights assignments, etc.
– Administrative Templates — contains settings for various Windows components. This includes standard Windows administrative templates and additional ADMX templates installed by the administrator (e.g., ADMX templates for managing Microsoft Office or Google Chrome). We recommend using a central store for administrative templates to simplify GPO management.
There is also a separate Preferences section containing additional Group Policy Preferences (GPP) settings that can be configured for client devices via GPO.
Close the policy editor and return to the GPMC console. All changes made to the GPO will apply to clients during the next group policy update cycle.
Select your GPO to view its key details. Four tabs are available:
– Scope — shows which OUs the policy is linked to. The Security Filtering section allows you to specify security groups for which the policy applies (by default, set to Authenticated Users, meaning the policy applies to all objects in the OU). The WMI Filtering section allows additional rules for filtering objects to which the GPO applies (see WMI filters for GPO).
– Details — contains basic GPO information (owner, creation and modification dates, version, GUID).
– Settings — displays a report of all configured GPO settings (similar to the output of the gpresult command).
– Delegation — shows current GPO permissions and allows modification.

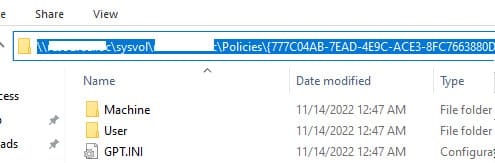
Active Directory stores GPOs as a set of files and folders in the SYSVOL directory, which is replicated across DCs. You can locate a specific GPO’s directory using its GUID (found in the Details tab) at the following UNC path: \\your-domain\sysvol\your-domain\Policies\{GUID}.
To stop a policy from applying to clients in a specific OU, you can either delete the link (Delete, which does not remove the GPO object itself) or temporarily disable it (Link Enabled = False).

The GPMC console also provides features for:
– Importing/exporting, backing up, and restoring GPOs.
– Generating Resultant Set of Policy (RSoP) reports.
– Remotely updating GPO settings on computers.
– Preparing GPOs for migration between domains.
We recommend familiarizing yourself with group policy principles to use them more effectively in managing Active Directory.