This article explains how to clear occupied COM ports in Windows and free up reserved ports for newly connected devices.
When you connect a new COM or certain USB devices (e.g., USB modem, mobile phone, Bluetooth adapter, or serial-to-USB converter) to your computer, Windows detects it via Plug-and-Play and assigns it a COM port number in the range of 1 to 255 (COM1, COM2, COM3, etc.). Upon reconnecting the same device, it is assigned the same previously reserved COM port number. New devices are assigned the first available COM port number. Some external devices may create multiple COM ports.
Issue with High COM Port Numbers
Some applications, especially older ones, can only address two-digit COM port numbers and may fail to work with ports like COM100 or higher, or may only recognize ports COM1-COM9. What can you do if a connected device is assigned a high COM port number? This article covers how to reset the numbering for reserved COM ports and remove unnecessary ports.
Changing a Device’s COM Port Number in Windows
In Windows, you can manually change the COM port number assigned to a device:
1. Open Device Manager with the command:
devmgmt.msc
2. From the menu, select View > Show hidden devices.
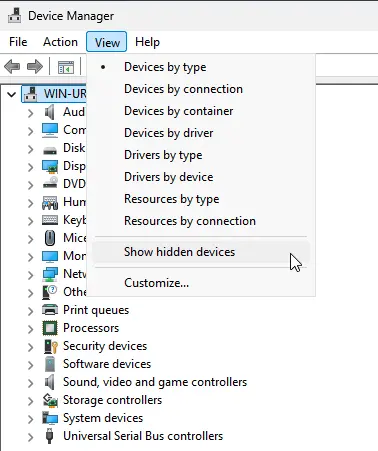
3. Expand Ports (COM & LPT) and locate the device in the list.
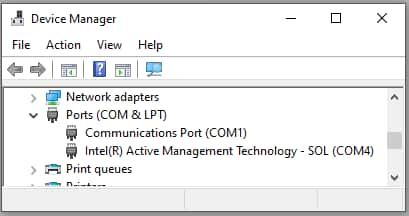
4. Go to the Port Settings tab in the device’s properties and click Advanced.
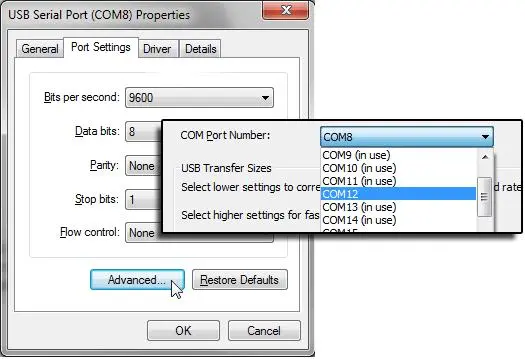
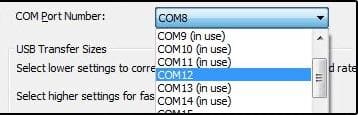
5. The current COM port number is shown in the COM Port Number field. To change it, select the desired number from the dropdown list.
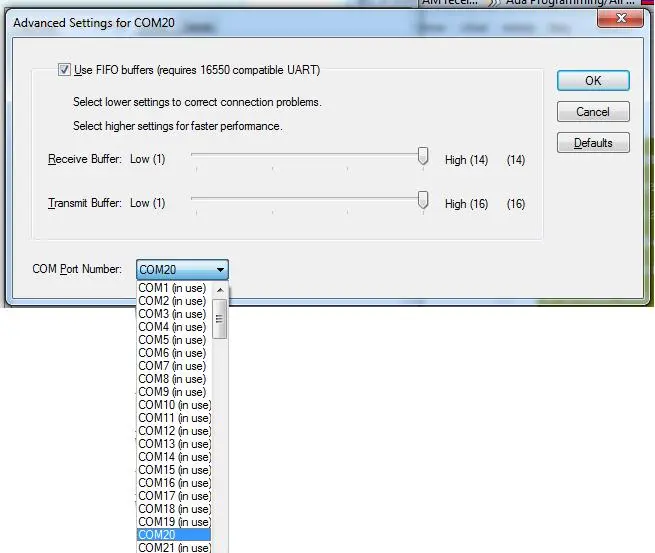
If the desired number is already in use, you need to remove the reservation for that COM port:
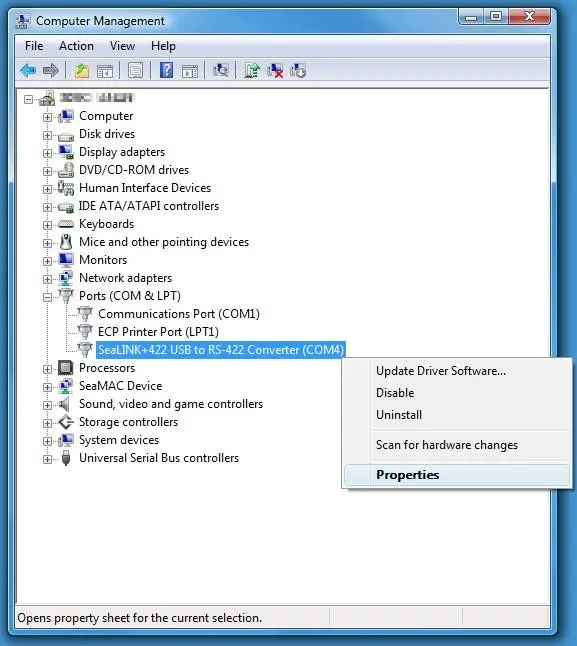
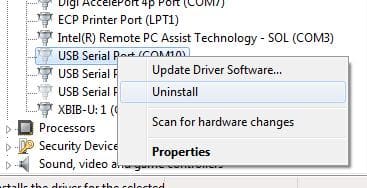
– Locate the device assigned the desired COM port number (a faded icon indicates the device is not connected).
– Right-click it and select Remove.
– Now assign the freed number to your device. Reopen the device’s properties, go to Port Settings > Advanced, and set the available COM port number.
Identifying Occupied COM Ports with PowerShell
You can list all occupied COM ports using PowerShell:
Get-WMIObject Win32_SerialPort | Select-Object Name,DeviceID,Description
To find the COM port number for a specific device by name:
Get-WMIObject Win32_SerialPort | Where-Object { $_.Name -like "*Arduino*"} | Select Name, DeviceID
Identifying the Process Using a COM Port in Windows
If a device is in use by a process, you cannot free the COM port. To identify the process, use the Process Explorer utility.
1. First, identify the service using the COM port with this PowerShell command:
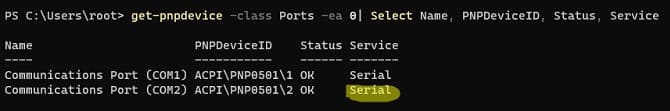
get-pnpdevice -class Ports -ea 0 | Select Name, PNPDeviceID, Status, Service
The service name for the COM port is listed in the Service column.
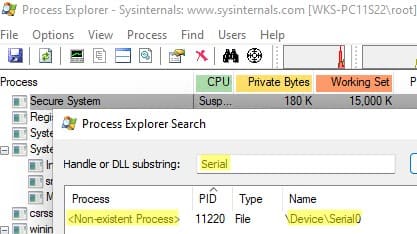
2. Launch Process Explorer with administrator privileges, select Find > Find Handle or DLL, enter the Service value, and terminate the process using the COM port.
Resetting Assigned COM Ports via the Registry
Information about used COM ports is stored in the registry at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\COM Name Arbiter.
Important! We strongly recommend creating a backup of this registry branch (File > Export). If something goes wrong, you can restore the original COM port configuration.
1. Open the Registry Editor with:
regedit.exe
and navigate to the specified branch.
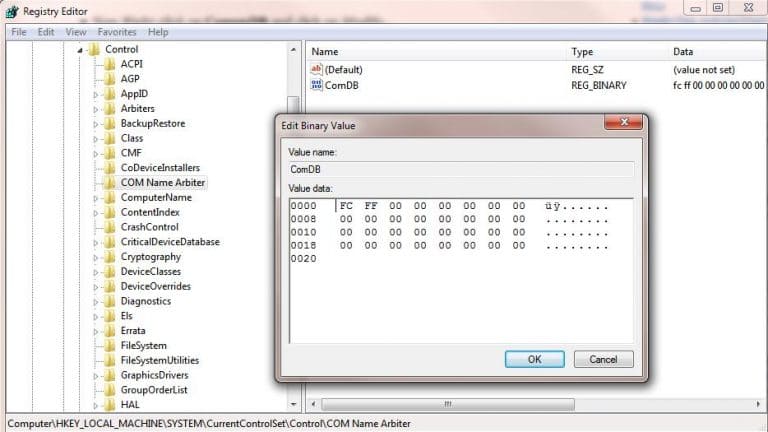
2. The ComDB parameter, in binary format, defines reserved ports. Each bit corresponds to the state of a port (1 to 255). For example, to reserve only COM3, the hex value of ComDB would be 04 (0000 0100).
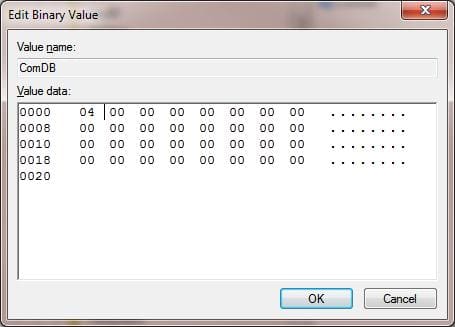
Important! Be extremely careful not to add extra bytes to this parameter, as it may cause the system to crash with a BSOD.
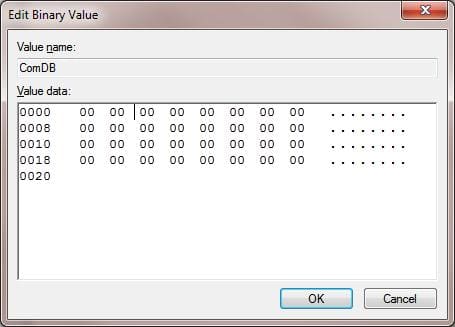
3. To completely reset all COM port assignments, set the ComDB key value to 0.
Note
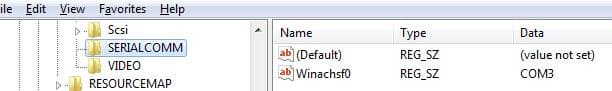
The HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\HARDWARE\DEVICEMAP\SERIALCOMM branch lists all COM ports available in Windows.
4. The HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Ports branch lists assigned COM ports. Remove all unnecessary ports (in our example, we keep only COM3 and delete the rest).
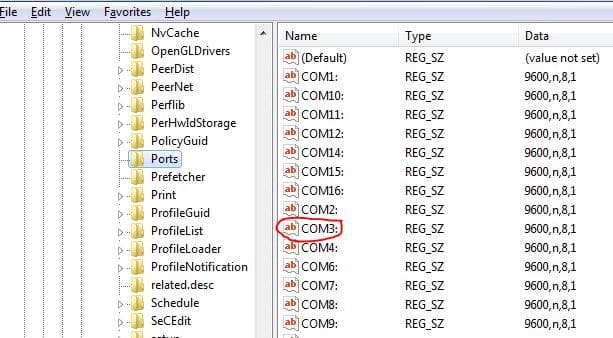
5. After completing these steps, disconnect all hardware and reboot Windows. After the reboot, reconnect the hardware in the desired order—all detected COM ports will be automatically assigned by the system.
Additional Tools for Clearing COM Ports
You can use the following free utilities to clear occupied COM ports:
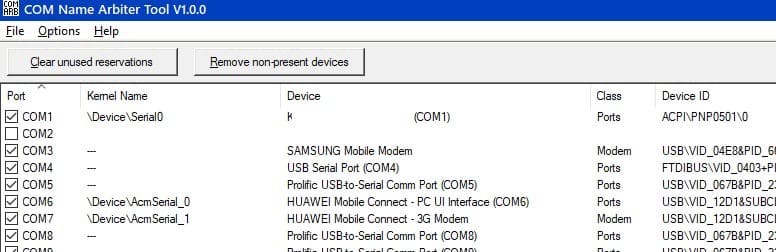
1. COM Name Arbiter Tool: A utility for freeing occupied COM ports. Run it with administrator privileges, select the desired ports, and click Clear unused Reservations.
2. Device Cleanup Tool: A utility for removing unused devices and clearing COM port reservations.