This article covers all possible solutions for resolving the user profile loading error on Windows 7, Windows 10, and Windows Server editions starting from 2008 (most commonly on RDS servers). This error is quite common and is typically caused by corruption in the user profile directory, but it can be resolved relatively easily.
Description of the Issue
The User Profile Service (ProfSvc) fails to load the Windows user profile, preventing the user from signing in.
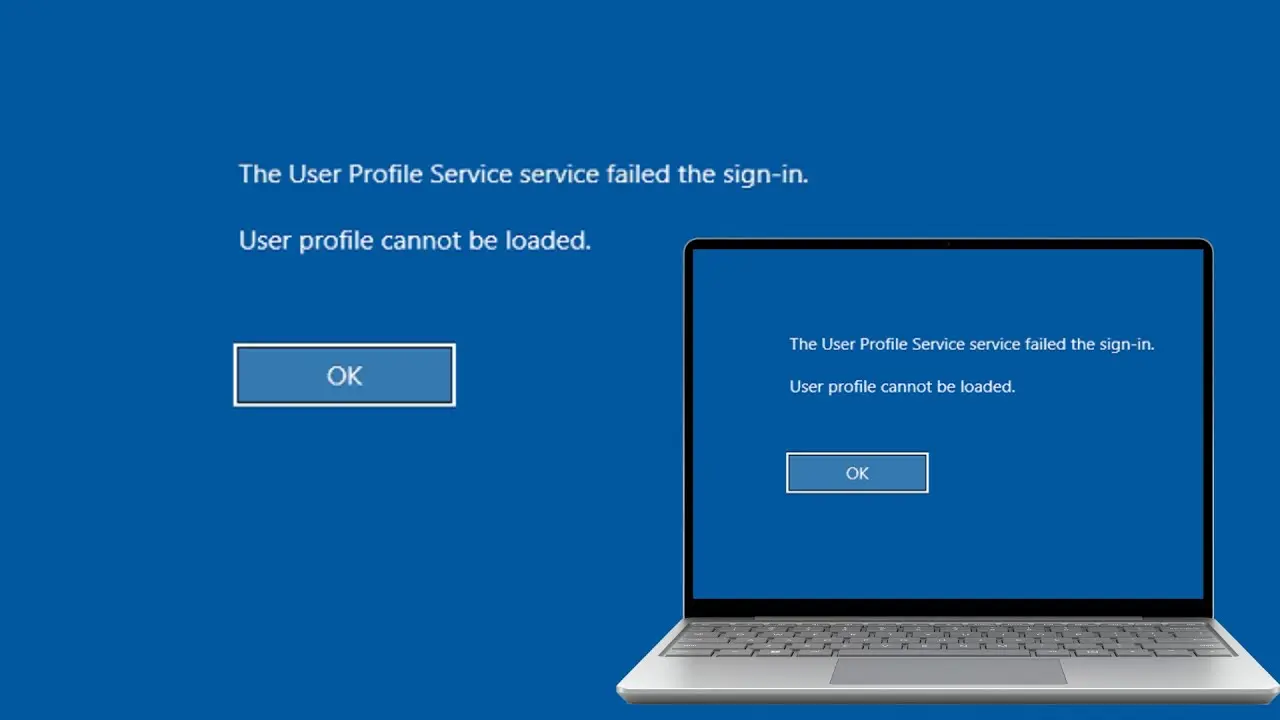
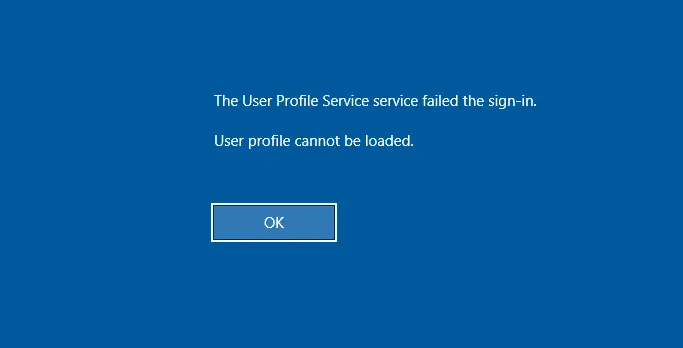
After entering credentials, the following message appears:
The User Profile Service failed the sign-in. User profile cannot be loaded.
You can purchase original product keys for Windows 10 or Windows 7 from our catalog:
Windows 10 – from 9.16 €
Windows 7 – from 7.50 €
This error is most often caused by corruption in the user profile or issues with permissions on the profile directory. It may occur due to improper system shutdown, system updates, or changes in the registry.
We will explore several methods to resolve the issue, starting with the simplest. You will need an account with administrative privileges on the computer to perform these actions.
1. Editing Profile Settings in the Registry
Launch the Registry Editor (regedit) with administrative privileges and navigate to the following registry branch:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList
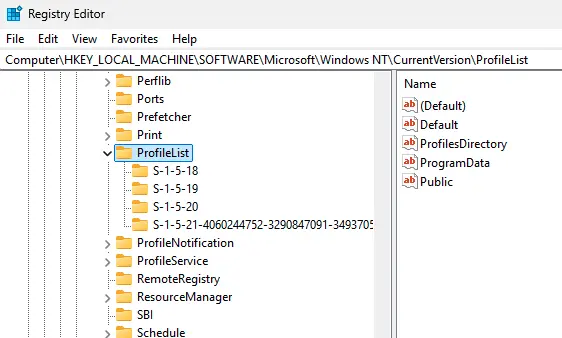
This section contains several folders named in the format S-1-5-21-xxxxxxx, which are Security Identifiers (SIDs) for users. You can identify the username associated with an SID using the following command to list local users and their SIDs:
wmic useraccount get domain,name,sid
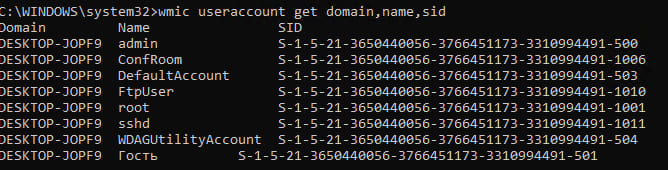
To locate the problematic user’s profile, check each section and find the ProfileImagePath parameter, which points to the specific user’s profile.
Possible Scenarios
– If the branch for the user’s profile ends with .bak, rename it by removing the .bak suffix.
– If there are two branches for the same profile—one with .bak and one without—rename the branch without .bak by adding, for example, .backup to its name. Then remove the .bak suffix from the other branch.
Next, modify the RefCount and State parameters, setting their values to 0. If these parameters do not exist, create them manually (type DWORD).
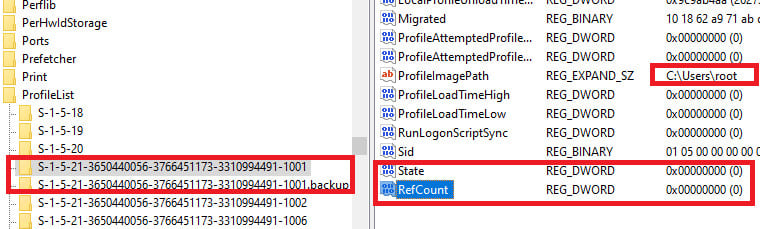
Ensure the ProfileImagePath value points to the correct profile directory and that the folder exists on the disk with the same name as specified in ProfileImagePath. In this example, it is C:\Users\root.
After making these changes, reboot the computer and try signing in with the user account.
2. Restoring the Default Profile by Replacing NTUSER.DAT
If the error occurs during a user’s first sign-in, the issue may be due to a corrupted NTUSER.DAT file in the Default profile. This file contains settings loaded into the user’s registry. If it is corrupted, the system cannot create a new profile.
1. Navigate to the C:\Users\Default directory.
2. Rename the NTUSER.DAT file (e.g., to NTUSER.DAT2).
3. Copy a valid NTUSER.DAT file from another user’s profile or from another computer running the same version of Windows.
Reboot the system. If the issue was caused by a corrupted NTUSER.DAT file, the error should be resolved.
3. Restoring the System from a Restore Point
If System Restore points are enabled, you can revert the system to a previous state when the error did not occur.
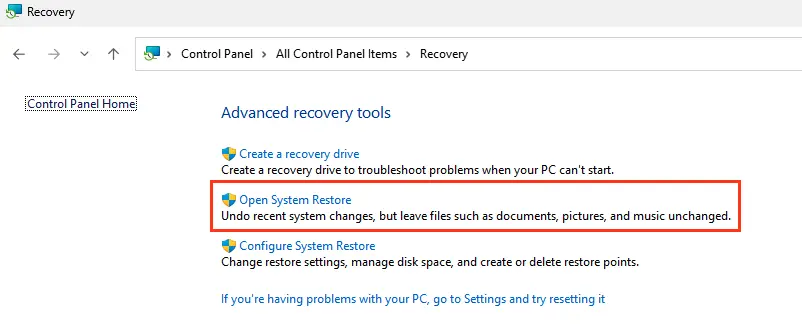
1. Go to Control Panel -> Recovery.
2. Click Open System Restore and follow the wizard’s instructions.
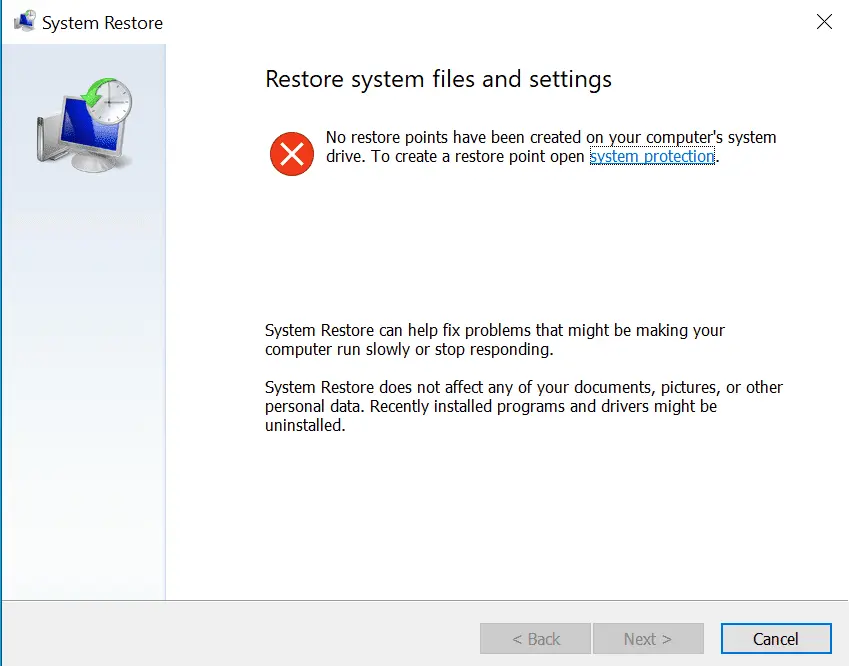
If System Restore is disabled, this method will not be available, and you will see the following error:
4. Creating a New User and Transferring Data
If the previous methods fail, create a new user and transfer data from the old profile:
1. Open a command prompt with administrative privileges and run:
netplwiz
2. Click Add.
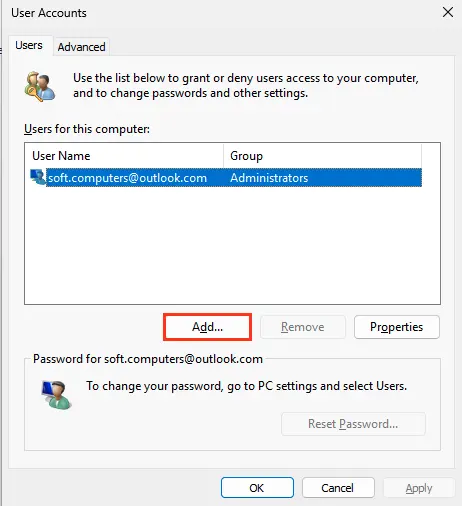
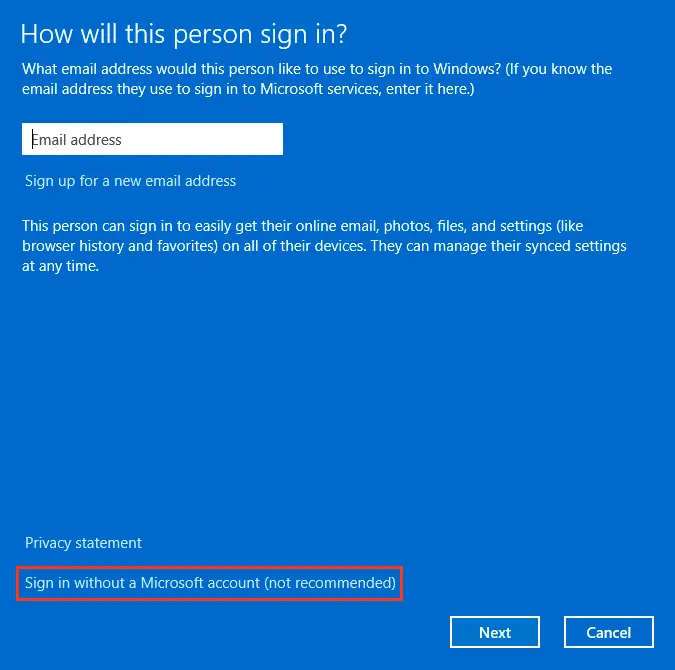
3. Select Sign in without a Microsoft account.
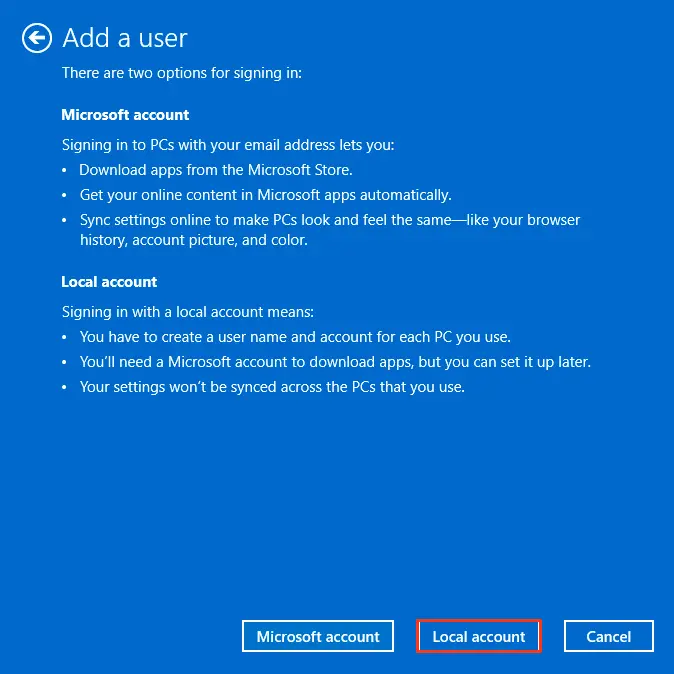
4. Choose Local account.
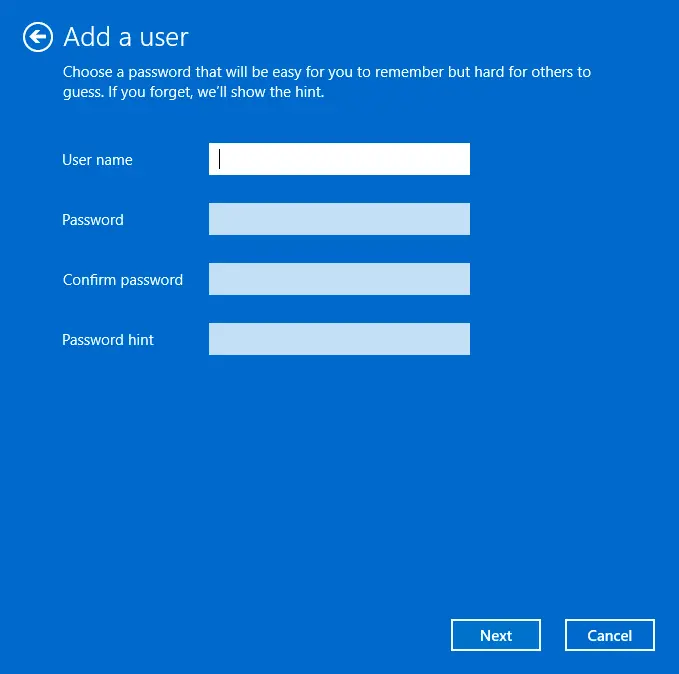
5. Enter a username and password, then click Next.
6. Copy the data from the old profile directory (C:\Users\old_profile) to the new profile directory.
Ensure hidden files and folders are visible.
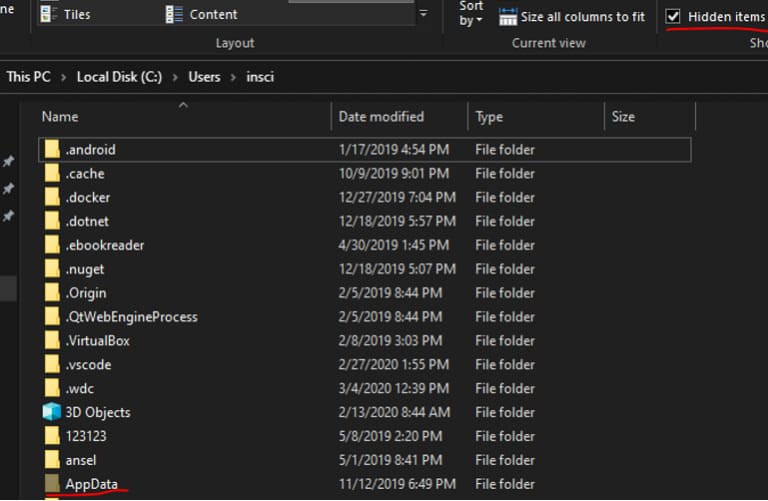
This method ensures you do not lose data from the old profile. If you encounter issues during copying, you can always access the old profile’s data by navigating to C:\Users\old_profile.
If you receive an access denied error when accessing the old profile folders, grant your new user account permissions to those directories.
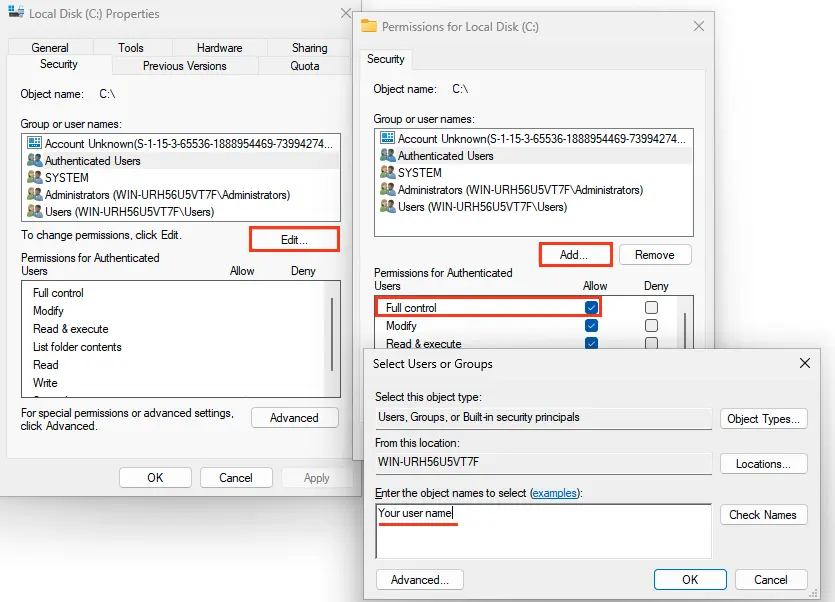
5. Resolving Permissions Issues on the Default Directory
On Windows Servers, the error may be caused by the Users group lacking read permissions on the C:\Users\Default directory. To resolve this:
1. Grant the Users group read permissions on the C:\Users\Default directory.
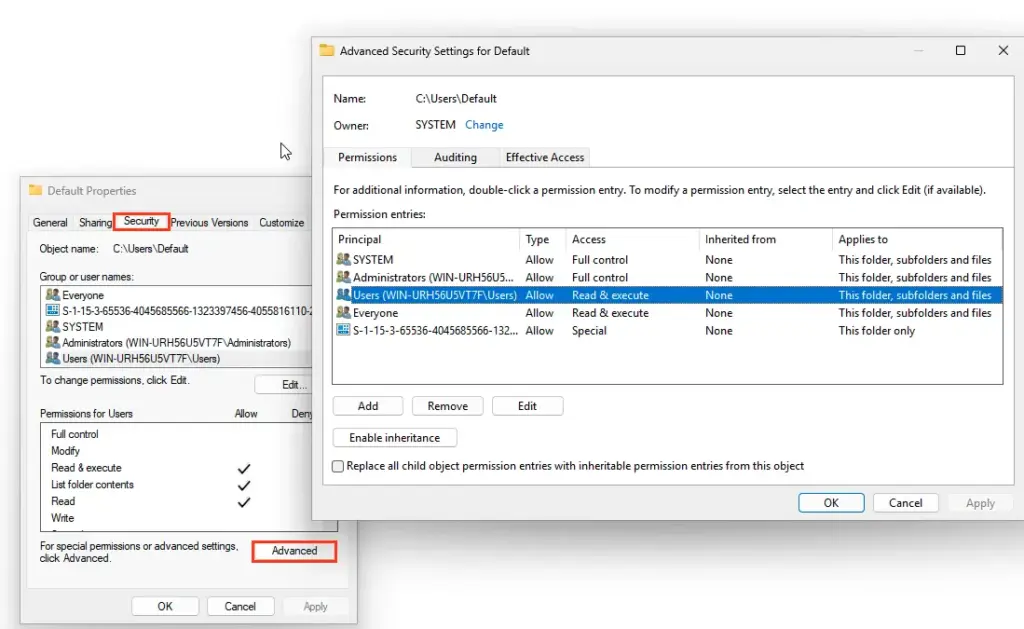
If the error persists, check the Windows Event Logs for errors with IDs 1509 and 1500.
Recommendations for Resolving the Issue
In most cases, the error is caused by incorrect profile data in the registry or a corrupted NTUSER.DAT file. Try correcting the profile paths in the registry and replacing the NTUSER.DAT file. These steps typically restore the profile’s functionality.
If you do not have another account with administrative privileges and the system does not create a temporary profile, use a bootable USB or installation disk to create a new account with administrative rights. Then follow the steps outlined in this article.