Deduplication is a well-known feature among professionals working with server editions of Windows. This mechanism significantly improves disk space efficiency by eliminating duplicate data. In client versions of Windows 10, this feature is not available by default, as home use cases typically do not involve storing large data arrays. However, it can be added manually, which is highly beneficial for professionals and enthusiasts looking to optimize resources and delay storage expansion. We previously covered enabling deduplication in Windows 8, and this experience has helped many users save significant costs.
At the release of Windows 10, deduplication was not supported, as the feature packages are derived from server editions. Server versions are developed with a slight delay compared to client versions, so when updating to a new build, note that deduplication packages may not yet be available.
Keep in mind that Windows 10 encompasses various operating systems, each requiring specific deduplication packages. Currently, the stable Semi-Annual Channel (SAC) releases of Windows 10 include:
| Version | Build | Release | Date end of Support | Deduplication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1507 (RTM) | 10240 | 29.07.2015 | 09.05.2017 | NO |
| 1511 | 10586 | 12.11.2015 | 10.10.2017 | YES |
| 1607 | 14393 | 02.08.2016 | 10.04.2018 | YES |
| 1703 | 15063 | 05.04.2017 | 09.10.2018 | YES |
| 1709 | 16299 | 17.10.2017 | 09.04.2019 | YES |
| 1803 | 17134 | 30.04.2018 | 12.10.2019 | YES |
| 1809 | 17763 | 13.11.2018 | 10.11.2020 | YES |
| 1903 | 18362 | 21.05.2019 | 08.12.2020 | YES |
| 1909 | 18363 | 12.11.2019 | 11.05.2021 | YES |
| 2004 | 19041 | 27.05.2020 | 14.12.2021 | YES |
This guide does not cover LTSC versions, as they are not intended for widespread distribution.
The first deduplication package for Windows 10 was developed for build 10514, based on Windows Server 2012 components. Later, packages based on Windows Server 2016 (14393) and Windows Server 2019 (17763) became available. Currently, server editions with a graphical interface have moved to the LTSC channel, with new releases every few years. The SAC channel includes a Windows Server version without a GUI, focused on rapid adoption of innovative technologies (e.g., containers, microservices).
As a result, intermediate Windows 10 versions without LTSC server counterparts receive deduplication packages from the SAC channel. This may impact stability, as SAC server versions are not designed for desktop use. There are reports of issues with packages for version 20.04, working on some systems but not others.
Note that deduplication is not supported in Insider Preview versions, so choose your priorities carefully.
A common concern is what happens to deduplicated volumes when upgrading from Windows 8 or between Windows 10 versions. Generally, data remains intact but inaccessible until the appropriate packages for the current OS build are installed.
Important: Deduplication in Windows 10 is an undocumented, unofficial feature. Its operation may be unstable or non-functional. While most scenarios pose no direct threat to data integrity, there is a risk of temporary data inaccessibility. Use this feature at your own risk.
Discussions about deduplication in Windows 10 and package distribution primarily occur on foreign resources, often with files hosted on third-party platforms. We have prepared our own archives and hosted them on our server for your convenience.
For each supported Windows 10 version, we provide the corresponding packages:
- Windows 10 1511 (10586)
- Windows 10 1607 (14393)
- Windows 10 1703 (15063)
- Windows 10 1709 (16299)
- Windows 10 1803 (17134)
- Windows 10 1809 (17763)
- Windows 10 1903/1909 (18362)
- Windows 10 2004 (19041)
Each archive contains core and language-specific packages (en-US, ru-RU). Install only one language package of your choice.
To install, open a Command Prompt with administrator privileges, navigate to the directory with the extracted packages, and run the commands. For example, for version 2004 (Russian):
dism /online /add-package /packagepath:Microsoft-Windows-FileServer-ServerCore-Package~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~10.0.19041.1.cab /packagepath:Microsoft-Windows-FileServer-ServerCore-Package~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~ru-RU~10.0.19041.1.cab
dism /online /add-package /packagepath:Microsoft-Windows-Dedup-Package~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~10.0.19041.1.cab /packagepath:Microsoft-Windows-Dedup-Package~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~ru-RU~10.0.19041.1.cab
dism /online /enable-feature /featurename:Dedup-Core /all
For other versions or languages, adjust the package names to match your build and language.
After successful installation, access to previously deduplicated data is restored without a reboot. There are no graphical tools for managing deduplication in Windows 10, so use PowerShell.
If enabling deduplication for the first time, import the Deduplication module:
Set-ExecutionPolicy ByPass -Force
Import-Module Deduplication
Check the status of volumes:
Get-DedupVolume
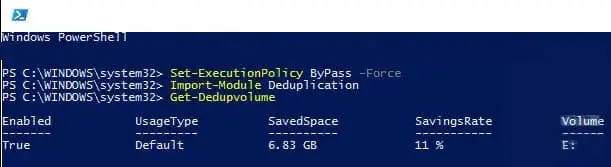
To enable deduplication on a specific volume:
Enable-DedupVolume -Volume E:
Without parameters, the volume defaults to “Default” usage. You can specify a usage type:
– HyperV: For virtual machine storage.
– Backup: For virtualized backup servers.
– Default: General purpose.
Example:
Enable-DedupVolume -Volume E: -UsageType HyperV
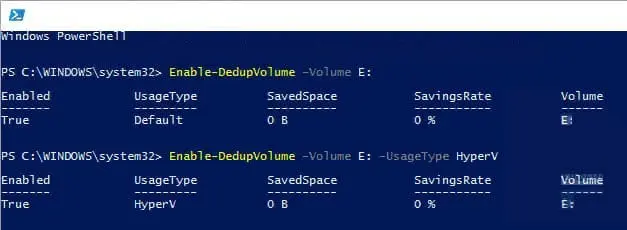
The enable command activates deduplication but does not optimize data. Data remains unoptimized until an optimization job runs.
Before starting optimization, configure parameters, such as the minimum file age for deduplication (in days). Lower values increase efficiency but raise system load.
For a minimum file age of 0 days:
Set-DedupVolume -Volume E: -MinimumFileAgeDays 0
Set a minimum file size, e.g., 512 MB (536870912 bytes):
Set-DedupVolume -Volume E: -MinimumFileSize 536870912
Options can be combined. Exclude specific folders:
Set-DedupVolume -Volume E: -ExcludeFolder E:\Folder1
To exclude additional folders, list them together, or the previous setting will be overwritten:
Set-DedupVolume -Volume E: -ExcludeFolder E:\Folder1,E:\Folder2
Exclude files by type:
Set-DedupVolume -Volume E: -ExcludeFileType tmp,lck
Start optimization:
Start-DedupJob -Volume E: -Type Optimization
Monitor progress:
Get-DedupJob
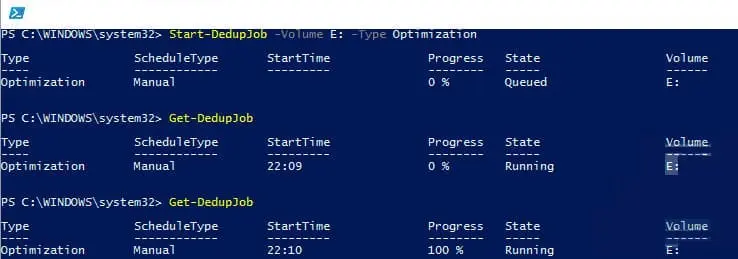
Other Start-DedupJob task types include:
1. Optimization: Data optimization.
2. Garbage Collection: Removes unused or deleted data blocks.
3. Scrubbing: Verifies data integrity.
4. Unoptimization: Reverts deduplication.
Initial optimization can be time-consuming and create significant disk load (approximately 20-40 MB/s), so plan operations accordingly.
Practical experience shows that deduplication is highly effective. For example, optimizing virtual machine storage can significantly delay the need for disk expansion.
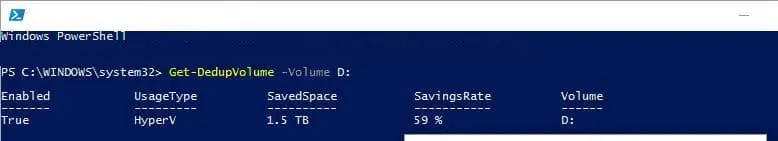
After setup, review and adjust the schedule for routine tasks to ensure they run when the computer is powered on. Some tasks are scheduled for late at night, which may not suit workstations.
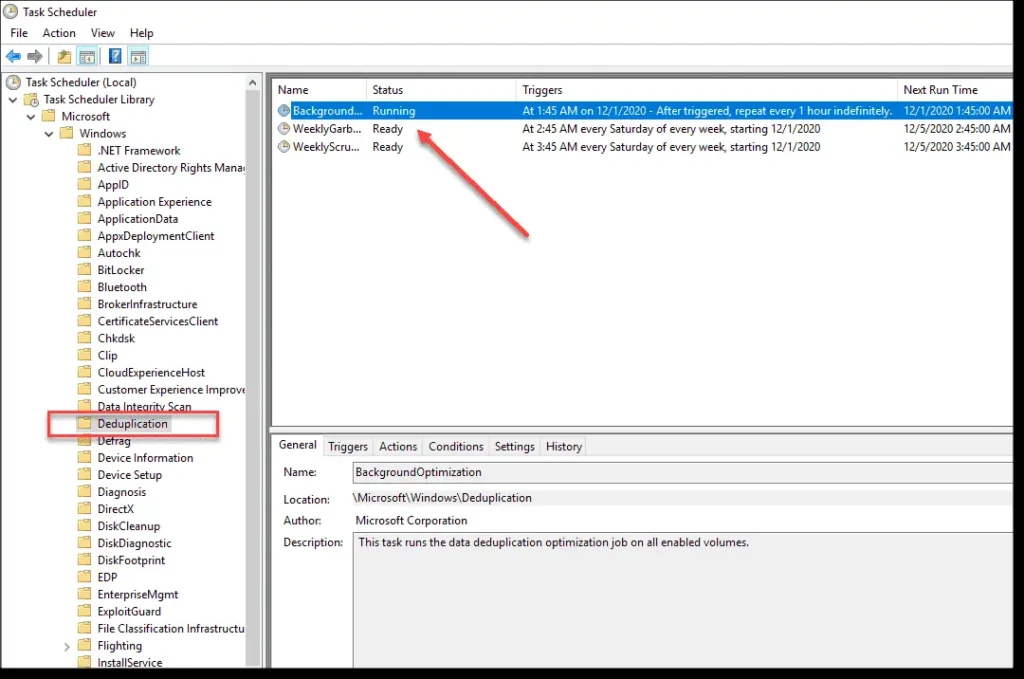
To disable deduplication, first perform an unoptimization to restore data to its original state:
Start-DedupJob -Volume E: -Type Unoptimization
If there’s insufficient space for restoration, the process will pause. Once complete, disable deduplication:
Disable-DedupVolume -Volume E:
Thanks to the efforts of enthusiasts, deduplication is available in Windows 10. While setup and management require technical knowledge and risk tolerance, the disk space savings and data management flexibility make it worthwhile, especially for professionals and enthusiasts comfortable with command-line operations.