This article explains how to check your computers’ compatibility with Windows 11 using PowerShell. We will use Microsoft’s official HardwareReadiness.ps1 script, available for download at: https://aka.ms/HWReadinessScript.
Minimum Requirements for Running Windows 11
1. Compatible x64 processor (full list of supported CPUs)
2. 4+ GB of RAM
3. Minimum disk size of 64 GB
4. Device with UEFI and Secure Boot enabled
5. Graphics card compatible with DirectX 12 and WDDM 2.0 drivers
6. TPM 2.0 module
7. Monitor with 720p resolution
Steps to Manually Check Computer Compatibility
1. Download the HardwareReadiness.ps1 script from https://aka.ms/HWReadinessScript.
2. Open Windows PowerShell with administrator privileges (the script uses the Get-WMIObject cmdlet, which is not supported in newer PowerShell Core versions).
3. Allow script execution for the current session:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope Process RemoteSigned
4. Run the script:
.\HardwareReadiness.ps1
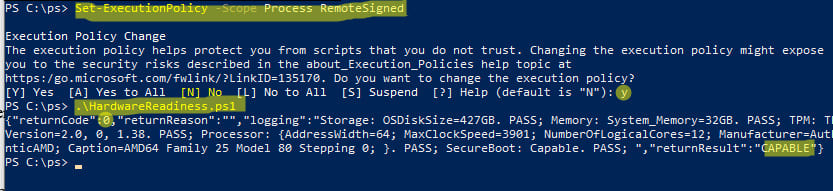
Script Execution Results
The script returns a code of 0 if the computer meets Windows 11 requirements (returnCode: 0, returnResult: CAPABLE):
{"returnCode":0,"returnReason":"","logging":"Storage: OSDiskSize=427GB. PASS; Memory: System_Memory=32GB. PASS; TPM: TPMVersion=2.0, 0, 1.38. PASS; Processor: {AddressWidth=64; MaxClockSpeed=3901; NumberOfLogicalCores=12; Manufacturer=AuthenticAMD; Caption=AMD64 Family 25 Model 80 Stepping 0; }. PASS; SecureBoot: Capable. PASS; ","returnResult":"CAPABLE"}
Bulk Compatibility Checking for Multiple Computers
To check compatibility across multiple corporate computers, tools like SCCM, Intune, or WSUS can be used to run third-party scripts. For a simpler approach, Group Policies can execute the script and store results in computer properties in Active Directory.
Modifying the Script to Store Results in AD
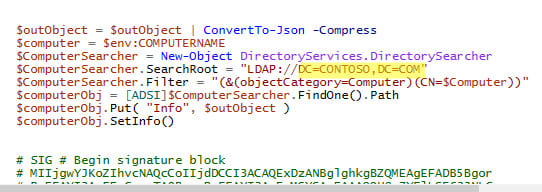
To write compatibility information to Active Directory, edit the HardwareReadiness.ps1 script and add the following code before the #SIG # Begin signature block section:
$outObject = $outObject | ConvertTo-Json -Compress
$computer = $env:COMPUTERNAME
$ComputerSearcher = New-Object DirectoryServices.DirectorySearcher
# Specify your domain name
$ComputerSearcher.SearchRoot = "LDAP://DC=CONTOSO,DC=COM"
$ComputerSearcher.Filter = "(&(objectCategory=Computer)(CN=$Computer))"
$computerObj = [ADSI]$ComputerSearcher.FindOne().Path
$computerObj.Put( "Info", $outObject )
$computerObj.SetInfo()
This code writes compatibility information to the Info attribute of the computer object in Active Directory.
Running the Script via GPO
1. Copy the script to the \\winitpro.loc\Netlogon folder on the domain controller.
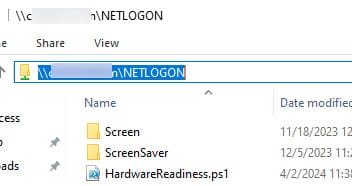
2. Open the Group Policy Management Console (gpmc.msc) and create a new GPO for the Organizational Unit (OU) containing the computers.
3. Navigate to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Scripts (Startup/Shutdown) > Startup, select the PowerShell Scripts tab, and specify the UNC path to the HardwareReadiness.ps1 script.
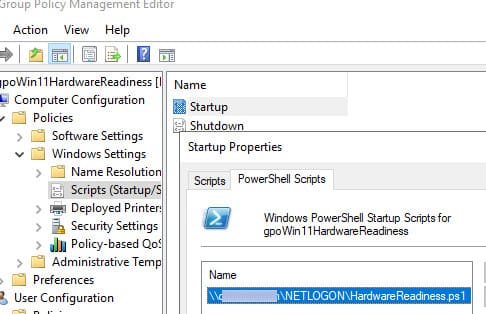
Enable the following policy settings:
– Configure Logon Script Delay and set a 1-minute delay for script execution.
– Always wait for the network at computer startup and logon in Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Logon.
Verifying Results in Active Directory
Restart the computer. Then, open the Active Directory Users and Computers console (dsa.msc), view the computer’s properties, and check the Attribute Editor tab to confirm that the Info attribute contains Windows 11 compatibility information.
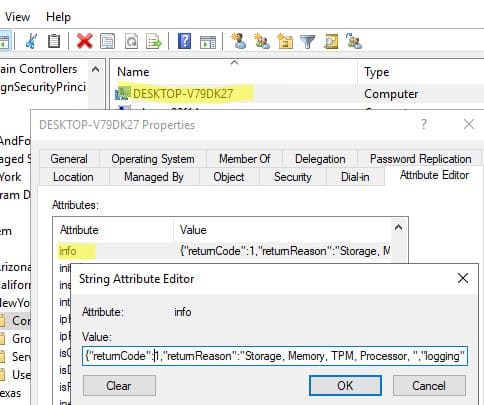
Retrieving Compatibility Information from Active Directory
After the logon script runs on all computers, retrieve information about compatible and incompatible computers using the Get-ADComputer cmdlet:
Get-ADComputer -Filter {enabled -eq "true"} -properties * | Where-Object {$_.info -ne $null}
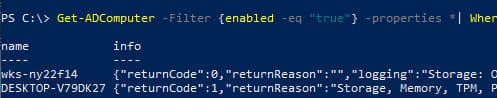
For detailed information about incompatible computers:
$Report = @()
$computers = Get-ADComputer -Filter {enabled -eq "true"} -properties * | Where-Object { $_.Info -match '"returnCode":1'}
foreach ($computer in $computers){
$jsonString = $computer.info
$object = $jsonString | ConvertFrom-Json
$returnReasonValues = $object.returnReason -split ', '
$CompInfo = [PSCustomObject]@{
"Computer" = $computer.name
"NonCompatibleItems" = $returnReasonValues
}
$Report += $CompInfo
}
$Report | fl
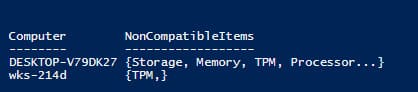
The ConvertFrom-Json cmdlet is used to parse data from JSON format.